Burmese (Cambodian) Translation

Target Language Translation Services provides high quality Burmese translation services, supplying technical, healthcare and automotive translation, localization and interpreting into and out of Burmese. We are a language services agency serving over 1,500 global companies. Our specialization, focus, industry-leading quality management standards and customer-centered attitude have earned us the trust of many of the world’s best technology, engineering, biomedical and pharmaceutical companies. For trusted, fast and precise Burmese translations, contact Target Language Translation Services for an online quote.
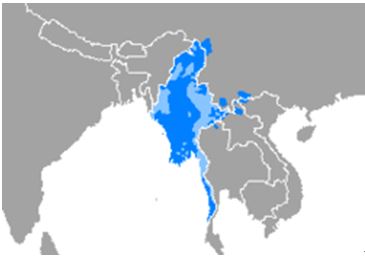
*Burmese-speaking areas
Did you know?
Burmese, or Myanmar, is a member of the Lolo-Burmese branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is spoken mainly in Myanmar (Burma), where it is the official language. In 2007 there were about 33 million people who spoke Burmese as a first language. There are also thought to be another 10 million who speak it as a second language.
Standard Burmese is spoken in the Irrawaddy River valley. Within that area there are minor variations in vocabulary and pronunciation between the Mandalay dialect of Upper Burma and the Yangon dialect of Lower Burma. Burmese dialects in other parts of Burma vary more from the standard, but they are all more or less mutually intelligible.
There are two registers of Burmese: high and low. The high register is utilized in formal literature, newspapers, radio and formal speeches. The low register is utilized in television, comics, informal literature, and everyday conversation. Since the 1960s some Burmese writers have promoted the use of the low register, and have suggest the abandoning of the high register.
The name Myanmar ([mjəmà]) is the high register name for the country, and Burma ( [bəmà]) is the low register name. Both names derive from the Bamar people ([bəmà lùmjó]), the largest ethnic group in Burma. The full official name of the country is the "Republic of the Union of Myanmar" ([pjìdàʊɴzṵ θàɴməda̰ mjəmà nàɪɴŋàɴdɔ̀]).
Dialects
It is spoken in most of the country with slight regional variations. According to Ethnologue, there are some varieties such as Beik (Merguese, Mergui), Mandalay Burmese, Yangon Burmese, and Yaw. In addition, there are other regional variants that vary from standard Burmese in pronunciation and vocabulary. All dialects are mutually intelligible. Standard Burmese is based on the dialect spoken in the lower valleys of the Irrawaddy and Chindwin rivers.
There are two registers: a formal and a colloquial one. The formal register is utilized in official publications, radio and TV broadcasts, literary works, and formal speech. The colloquial register is utilized in daily communications.
Sound system
Like all Sino-Tibetan languages, Burmese has a simple syllable structure consisting of an initial consonant followed by a vowel with an associated tone. There are no final consonants.
Tones
Burmese is a tonal language. This means that all syllables have prosodic features that are an integral part of their pronunciation and that affect word meaning. Prosodic contrasts involve not only pitch, but also phonation, intensity (loudness), duration, and vowel quality. According to one analysis, Burmese has 4 tones (examples below are taken from Wikipedia):
|
Tone |
Notation |
Description |
Example |
|
Low |
à |
low pitch |
kʰà ‘shake’ |
|
High |
á |
slightly breathy, high pitch |
kʰá ‘be bitter’
|
|
Creaky |
a~ |
Tense or creaky, high pitch |
kʰa~ ‘fee’
|
|
Checked |
aʔ |
final glottal stop, high pitch |
kʰaʔ ‘draw off’ |
The Burmese or Myanmar script developed from the Mon script, which was adapted from a southern Indian script during the 8th century. The earliest known inscriptions in the Burmese script date from the 11th century.
Notable Features
•Type of writing system: syllabic alphabet - each letter has an inherent vowel [a]. Other vowels sounds are indicated using separate letters or diacritics which appear above, below, in front of, after or around the consonant.
•The rounded appearance of letters is a result of the use of palm leaves as the traditional writing material. Straight lines would have torn the leaves. The Burmese name for the script is ca-lonh 'round script'.
•Burmese is a tonal language with three main tones (high, low and creaky) and two other tones (stopped and reduced). The tones are indicated in writing using diacritics or special letters.
•Used to write: Burmese/Myanmar, Karen and Mon.

Vocabulary
Hinduism and Buddhism have had a profound religious and linguistic effect on Burmese. As a result, learned or specialized words which came into the spoken language through the written one often contain Pali loanwords, similar to Latinate words in English. British rule (1886-1937) brought a large number of English words into the language, particularly those related to business, technology, science and politics. As a result, sometimes there are competing terms, one borrowed and one native, for instance, telibihyn and yoʔmiyin θanea, literally ‘image-see sound-hear’, i.e, ‘television’. New words are normally formed from native elements through compounding, prefixation and reduplication.
Below are a few words and phrases in Burmese (in transliteration)
Formal greeting at any time of the day Mingâlaba (formal)
Good bye Thwa dau me
Please Kyeizu pyu yue
Thank you Kyeizu tin ba de
Yes. Hode
No. Mahobu
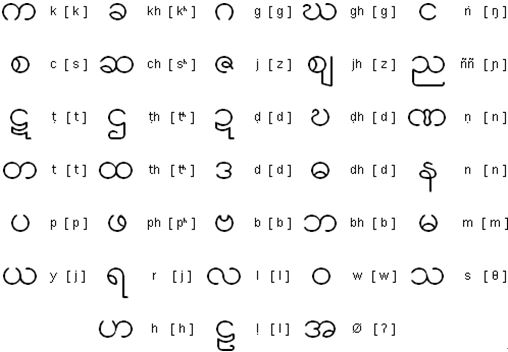
Consonants
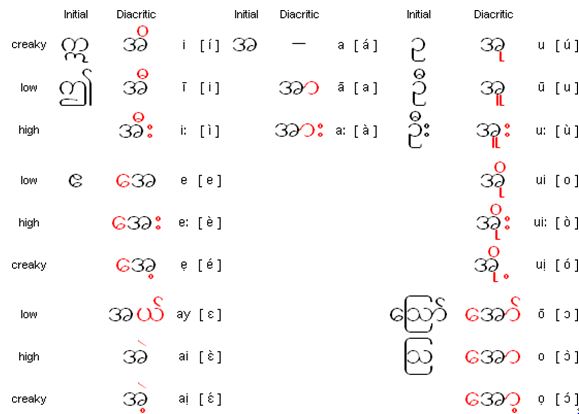
Vowels and vowel diacritics
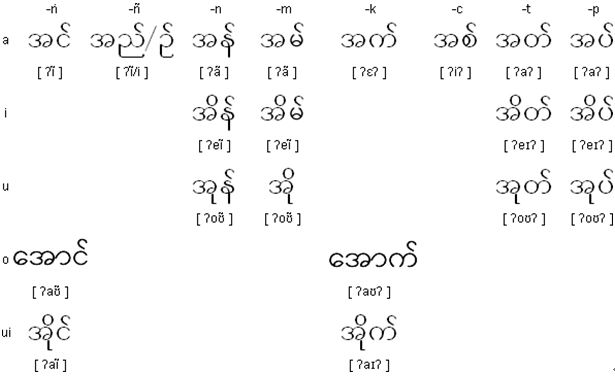
Regular Rhymes
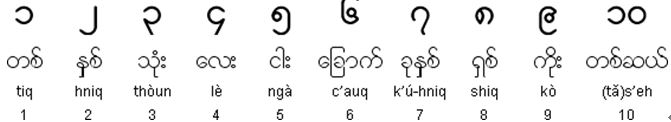
Numerals
Just contact us to get more information and a no-obligation quote. Our project managers can be reached via telephone, email, or the form. We look forward to serving you.
For more information about Burmese (Cambodian),
call us or add wechat today at +86-13616034782
or send us an email to:info@target-trans.com