Arabic Translation
If you’re planning to move to the Gulf region to study, or you’re ready to expand your business to the Middle East, we’re here to help. Whether you need an Arabic linguist for your financial documents, an Arabic interpreter for your marketing conference, or even a complete Arabic localization service for your e-commerce site, Target Language Translation Services has the language professionals that will help you globalize your brand.
Use of Arabic as the sole official language (green) and an official language (blue)
The Arabic script evolved from the Nabataean Aramaic script. It has been utilized since the 4th century AD, but the earliest document, an inscription in Arabic, Syriac and Greek, dates from 512 AD. The Aramaic language has fewer consonants than Arabic, so during the 7th century new Arabic letters were created by adding dots to existing letters in order to avoid ambiguities. Further diacritics indicating short vowels were introduced, but are only generally used to ensure the Qur'an was read aloud without errors.
There are two main types of written Arabic:
1.Classical Arabic - the language of the Qur'an and classical literature. It varies from Modern Standard Arabic mainly in style and vocabulary, some of which is archaic. All Muslims are expected to recite the Qur'an in the original language, however many rely on translations in order to understand the text.
2.Modern Standard Arabic (اللغة العربية الفصحى / al-luġatu l-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā) - the universal language of the Arabic-speaking world which is comprehended by all Arabic speakers. It is the language of the vast majority of written material and of formal TV shows, lectures, etc.
Each Arabic speaking country or region also has its own variety of colloquial spoken Arabic. These colloquial varieties of Arabic appear in written form in some poetry, cartoons and comics, plays and personal letters. There are also translations of the bible into most varieties of colloquial Arabic.
Arabic has also been written with the Hebrew, Syriac and Latin scripts.
Notable Features
•Type of writing system: abjad
•Direction of writing: words are written in horizontal lines from right to left, numerals are written from left to right
•Number of letters: 28 (in Arabic) - some additional letters are used in Arabic when writing placenames or foreign words containing sounds which do not occur in Standard Arabic, such as /p/ or /g/. Additional letters are used when writing other languages.
•Used to write: Arabic, Adamaua Fulfulde, Afrikaans, Arabic (Algerian), Arabic (Egyptian), Arabic (Hassaniya), Arabic (Lebanese), Arabic (Modern Standard), Arabic (Moroccan), Arabic (Syrian), Arabic (Tunisian), Arwi, Äynu, Azeri, Balti, Baluchi, Beja, Belarusian, Bosnian, Brahui, Chagatai, Chechen, Comorian, Crimean Tatar, Dargwa, Dari, Dogri, Domari, Gilaki, Hausa, Hazaragi, Indus Kohistani, Kabyle, Karakalpak, Konkani, Kashmiri, Kazakh, Khowar, Khorasani Turkic, Kurdish, Kyrgyz, Lezgi, Luri, Malay, Mandinka, Marwari, Mandekan, Mazandarani, Morisco, Mozarabic, Ormuri, Palula, Parkari Koli, Pashto, Persian/Farsi, Punjabi, Qashqai, Rajasthani, Rohingya, Salar, Saraiki, Serer, Shabaki, Shina, Shughni, Sindhi, Somali, Tatar, Tausūg, Tawallammat Tamajaq, Tayart Tamajeq, Torwali, Turkish, Urdu, Uyghur, Uzbek, Wakhi, Wolof and a number of other languages
•Most letters change form depending on whether they appear at the beginning, middle or end of a word, or on their own. (see below)
•Letters that can be joined are always joined in both hand-written and printed Arabic. The only exceptions to this rule are crossword puzzles and signs in which the script is written vertically.
•The long vowels /a:/, /i:/ and /u:/ are represented by the letters 'alif, yā' and wāw respectively.
•Vowel diacritics, which are used to mark short vowels, and other special symbols appear only in the Qur'an. They are also utilized, though with less consistency, in other religious texts, in classical poetry, in books for children and foreign learners, and occasionally in complex texts to avoid ambiguity. Sometimes the diacritics are used for decorative purposes in book titles, letterheads, nameplates, etc.
Arabic script
Arabic consonants
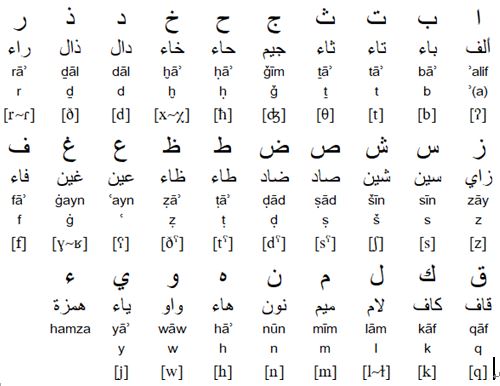
The transliteration of consonants used above is the ISO version of 1984. There are diffeent other ways of transliterating Arabic.
This chart shows how the letters change in different positions

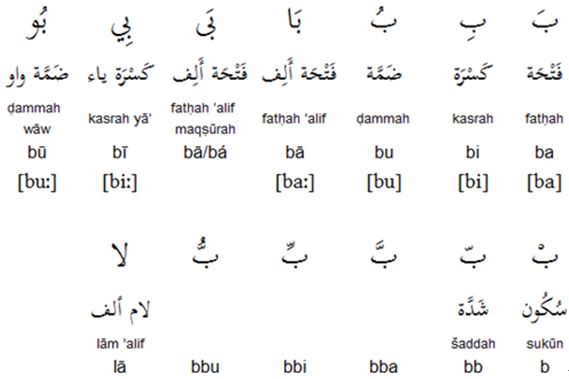
Arabic vowel diacritics and other symbols
Arabic chat alphabet
When chatting online some Arabic speakers write in the Latin alphabet use the following letters:

These numerals are those used when writing Arabic and are written from left to right. In Arabic they are known as "Indian numbers" (أرقام هندية / arqa-m hindiyyah). The term 'Arabic numerals' is also used to refer to 1, 2, 3, etc.
The Arabic language
Arabic is a Semitic language with about 221 million speakers in Afghanistan, Algeria, Bahrain, Chad, Cyprus, Djibouti, Egypt, Eritrea, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kenya, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Oman, Palestinian West Bank & Gaza, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Tanzania, Tunisia, Turkey, UAE, Uzbekistan and Yemen.
There are over 30 different varieties of colloquial Arabic which include:
•Egyptian - spoken by about 50 million people in Egypt and perhaps the most widely understood variety, thanks to the popularity of Egyptian-made films and TV shows.
•Algerian - spoken by about 22 million people in Algeria
•Moroccan/Maghrebi - spoken in Morocco by about 19.5 million people
•Sudanese - spoken in Sudan by about 19 million people
•Saidi - spoken by about 19 million people in Egypt
•North Levantine - spoken in Lebanon and Syria by about 15 million people
•Mesopotamian - spoken by about 14 million people in Iraq, Iran and Syria
•Najdi - spoken in Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Jordan and Syria by about 10 million people
For a full list of all varieties of colloquial Arabic click here (format: Excel, 20K).
Arabic words in English
There are many words of Arabic origin in English, spread over a variety of fields. Most of them have entered English through other languages, notably French and Spanish. Below is a small sampling of Arabic loanwords. One can easily find English words starting with al– (the definite article in Arabic) in everyday English, e.g., algebra, alcohol, alcove.
|
English word |
from Arabic |
|
adobe |
al-tob, ‘the brick’ |
|
albacore |
al bakara, ‘the young camels’ |
|
alcove |
al-qobbah, ‘the vaulted chamber’ |
|
alfalfa |
al-fisfisa, ‘the fresh fodder’ |
|
algebra |
al jebr, ‘reunion of broken parts’ (as in computation) |
|
arsenal |
dar as-sina’ah, ‘house of manufacture, workshop’ |
|
artichoke |
al-kharshof, ‘the artichoke’ |
|
ayatollah |
ayatu-llah, ‘miraculous sign of God’ |
|
carob |
kharrub, ‘locust bean pod’ |
|
coffee |
qahwah, ‘coffee’ |
|
cipher |
sifr, ‘zero, empty, nothing |
|
cotton |
qutn, ‘cotton |
|
emir |
amir, ‘commander’ |
|
fedayeen |
plural of fedai, ‘devotee, zealot, one who risks life for a cause’ |
|
ghoul |
ghul, ‘evil spirit that robs graves and feeds on corpses’ |
|
harem |
haram, ‘women’s quarters’ |
|
hashish |
hashish, ‘powdered hemp,’ literally ‘dry herb’ |
|
imam |
imam, ‘leader, one who precedes’ |
|
Islam |
islam, ‘submission’ (to the will of God) |
|
jihad |
jahada, ‘he waged war’ |
|
kismet |
qismah, qismat, ‘portion, lot, fate’ |
|
Koran (Qur’an) |
qur’a, ‘a reading, recitation, book’ |
|
lime |
limah, ‘citrus fruit’ |
|
mask |
maskhara, ‘buffoon’ |
|
mosque |
masjid ‘temple, place of worship’ |
|
mullah |
mawla ‘master’ |
|
mummy |
mumiyah ’embalmed body’ |
|
Muslim |
muslim, one who submits’ (to the faith) |
|
safari |
safar, ‘journey’ |
|
Sahara |
çahra, ‘desert’ |
|
sheikh |
shaykh, ‘chief,’ literally, ‘old man’ |
|
Shiite |
shi’ah, ‘ followers,’ members of the Shia sect of Islam who recognize Ali, Muhammad’s son-in-law, as the lawful successor of the Prophet |
|
sofa |
suffah, ‘bench’ |
|
sugar |
sukkar |
|
Sunni |
sunna “traditional teachings of Muhammad,” Muslims who accept the orthodox tradition as well as the Qu’ran |
|
tariff |
taarif, ‘inventory of fees to be paid’ |
Just contact us to get more information and a no-obligation quote. Our project managers can be reached via telephone, email, or the form. We look forward to serving you.
For more information about Arabic translation,
call us or add wechat today at +86-18206071482
or send us an email to:info@target-trans.com