Dutch Translation

Are you looking for a regular or certified translation to or from Dutch? Target Language Translation Services delivers instant Dutch translation whatever your needs may be. We can provide you with Dutch translations from a multitude of languages. Our specialized and experienced native speakers, regular of certified Dutch linguists and specialized rich dictionaries built into the software can assist you with all of your documents, whether you need them for business or personal matters. Besides the Dutch language, our Dutch linguists are also experts in the Dutch culture and experienced in translating documents for all kinds of businesses, sectors or branches of industry and commerce. You can entrust our certified Dutch translation agency with all your confidential correspondence and legal and financial documents. Get your free quote now!
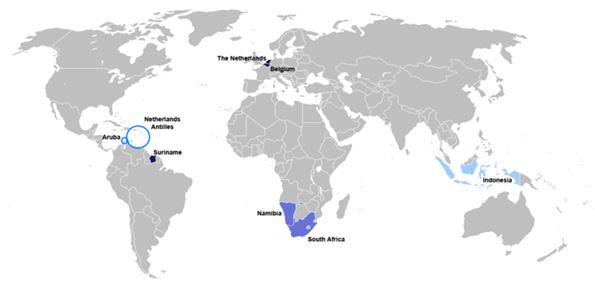
Dutch-speaking world (included are areas of daughter language Afrikaans)
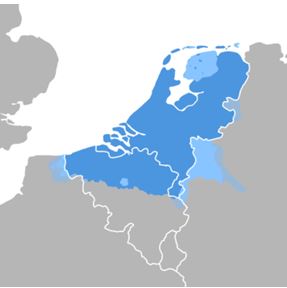
Distribution of the Dutch language in Western Europe
Introduction of Dutch
Dutch is a West Germanic language with about 24 million speakers, mainly in the Netherlands and Belgium. There are about 16 million Dutch speakers in the Netherlands, where it is the official language. There are about 7.6 million Dutch speakers in Belgium, mainly in Antwerp, East Flanders, Flemish Brabant and Limburg provinces, and also in Brussels.
Dutch is spoken in Curaçao, Aruba, Sint Maarten and elsewhere in the Caribbean Netherlands by about 19,760 people. There are about 126,200 Dutch speakers in Suriname, and in Indonesia some lawyers know Dutch as certain legal codes written in Dutch. Other countries with significiant numbers of Dutch speakers include Germany (151,000), the USA (142,000) and Canada (103,000).
The official or standard form of Dutch is known as Algemeen Beschaafd Nederlands (ABN), 'General Civilized Dutch'. It is taught in schools and used by authorities in the Netherlands, Flanders (Belgium), Suriname and the Netherlands Antilles. An association known as the Taalunie (Language Union), which was set up by governments of the Netherlands and Flanders, regulates the orthography and spelling of ABN. Alternative names for ABN are Algemeen Nederlands (AN), General Dutch, and Standaardnederlands, Standard Dutch.
The Dutch dialects spoken in Belgium are collectively known as Flemish (Vlaams). They differ to some extent from the Dutch spoken in the Netherlands in terms of intonation and pronunciation, and there are minor differences in vocabulary, including loanwords from French and English not found in Standard Dutch.
The Dutch language developed from the Lower Franconian (Niederfränkisch) dialect of Low German. The earliest known example of written Old Franconian appears in a 9th century Latin manuscript, the Laws of the Salic Franks, and in translations of the Psalms. Some poetry written in Middle Dutch dating from the 12th and 13th centuries survives. The Dutch translation of the Bible, the Staten-Bijbel, of 1619-1637 was one of the first major works in Modern Dutch.

Dutch alphabet (Nederlands alfabet)

Note
There is also a digraph, IJ ij (lange ij), which was once written Y y, a letter which is now mainly utilized in foreign loanwords. Y is also known as Griekse ij, i-grec or ypsilon. ij is sometimes written with accents on both parts (íj́).
Dutch pronunciation (Nederlandse uitspraak)

Notes
• b = [p] at the end of a word, [b] elsewhere
• d = [t] at the end of a word, [d] elsewhere
• e = [ə] in unaccented syllables
• g = [x] at the start of a word, [ʁ] elsewhere in some parts of the Netherlands. In some dialects, g = [ɣ]
• r is usually silent before g. Elsewhere = [r]. In some dialects, r = [ʁ] or [ʀ]
• An acute accent (é) is used to emphasise a word or phrase, and on vowels in stressed syllables.
For example, Ik wil het nú! = I want it now! It can also be used to differentiate homographs. For example, een = a(n) and één = one, and voor = for, vóór = before.
• A grave accent (à) is used to indicate stress on short vowels. For example, Kàn jij dat? = Can you do that?
• A diaeresis is used to two vowels are pronounced separately, rather than as a diphthong. For example, zeeën = seas, reëel = realistic.
• Acute, grave and circumflex (â) accents appear in French loanwords, such as carrière (career), café and enquête (survey).
• An apostrophe (or single quote) is used to indicate the omission of parts of words. For example m’n / m'n = mijn (my)
• Other letters appear in non-native vocabulary or words using older, obsolete spellings, especially in personal names. For details, see: wikipedia.org/wiki/Dutch_orthography
How much does a translation into Dutch cost?
The standard rate for translations from English into Dutch is $ 0.14. For urgent jobs that need several linguists working simultaneously, we will apply a surcharge.
Just contact us to get more information and a no-obligation quote. Our project managers can be reached via telephone, email, or the form. We look forward to serving you.
For more information about Dutch translation,
call us or add wechat today at +86-13616034782
or send us an email to:info@target-trans.com