Vietnamese Translation

Certified Vietnamese to English translations are most often required for submission to the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services. Meanwhile, many other institutions such as courts, universities and state and federal agencies may also request a certified translation from Vietnamese to English of documents originally in Vietnamese.
If you require professional language services in Vietnamese, Target Language Translation Services offers a complete set of solutions to satisfy the needs of its worldwide clients. All Vietnamese translation services are performed by certified human linguists who are native Vietnamese speakers and are fluent in English with an average of 5-10 years of experience offering professional translation services.
*Natively Vietnamese-speaking (non-minority) areas of Vietnam
About Vietnamese
Vietnamese is a member of the Vietic branch of the Austroasiatic language family. It is spoken mainly in Vietnam, and in Guangxi Province in southern China, and in Cambodia and Laos. There are also significant numbers of Vietnamese speakers in France, Australia, and the USA. In 2007 there were about 75 million speakers of Vietnamese.
Traditionally Vietnamese is classified as a member of the Mon-Khmer branch of the Austroasiatic language family. However, recently linguists have proposed that Vietnamese and Muong should be classified as a separate branch of that family, called Vietic or Viet-Muong.
Vietnamese is the official language of Vietnam, and is spoken by the majority of the population as a native language. Ethnic minority groups speak it as a second language. Vietnamese is also recognized as a minority language in the Czech Republic
Written Vietnamese
During the period when Vietnam was dominated by China (939-1919) the main written language used, at least at first, was Classical Chinese (chữ nho), while Vietnamese was an oral language. Chinese texts were read with Vietnamese pronunciation, and many Chinese words were borrowed into Vietnamese, to create a Sino-Vietnamese form of language.
From about the 13th century, Vietnamese was written with a script adapted from Chinese known as Chữ-nôm or Nôm. At first most Vietnamese literature was essentially Chinese in structure and vocabulary. Later literature developed a more Vietnamese style, but was still full of Chinese loan words. The greatest literary work in Vietnamese is Kim Van Kieu, the 'Tale of Kieu', a romance written by Nguyen-Du (1765-1820).
Chữ-nôm was used until the 20th century. Courses in the Chữ-nôm script were available at Ho Chi Minh University until 1993, and the script is still studied and taught at the Han-Nôm Institute in Hanoi, which has recently published a dictionary of all the nôm characters.
During the 17th century, Roman Catholic missionaries introduced a Latin-based orthography for Vietnamese, Quốc Ngữ (national language),which has been used ever since. Until the early 20th century, Quốc Ngữ was used in parallel with Chữ-nôm. Today only Quốc Ngữ is used.
Vietnamese alphabet and pronunciation

Notes
• The letters "F", "J", "W" and "Z" are not part of the Vietnamese alphabet, but are used in foreign loan words. "W" (vê-đúp)" is sometimes used in place of "Ư" in abbreviations. In informal writing, "W", "F", and "J" are sometimes used as shorthands for "QU", "PH" and "GI" respectively.
• The digraph "GH" and the trigraph "NGH" are basically replacements for "G" and "NG" that are used before "I", in order to avoid confusion with the "GI" digraph. For historical reasons, they are also used before "E" or "Ê".
• G = [ʒ] before i, ê, and e, [ɣ] elsewhere
• D and GI = [z] in the northern dialects (including Hanoi), and [j] in the central, southern and Saigon dialects.
• V is pronounced [v] in the northern dialects, and [j] in the southern dialects.
• R = [ʐ, ɹ] in southern dialects
Tones
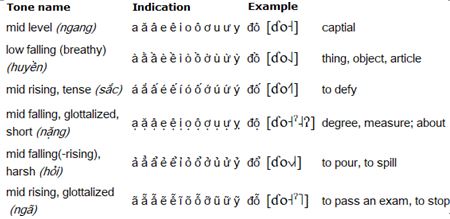
Northern varieties of Vietnamese have the following six tones: varieties have five tones.
In central and southern varieties of Vietanamese, the nặng tone, which is pronounced [˨˧], and the ngã tone is replaced with the hỏi tone by many people.
How much does a translation into Vietnamese cost?
The standard rate for translations from English into Vietnamese is $ 0.10. For urgent jobs that need several linguists working simultaneously, we will apply a surcharge
For more information about Vietnamese translation,
call us or add wechat today at +86-13616034782
or send us an email to:info@target-trans.com